Taxonomy
- Kingdon: Animalia

Capybara Family from the San Diego Zoo. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species lists the capybara as a least concern species.
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Rodentia
- Family: Caviidae
- Genus: Hydrochoerus
- Species: Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris
Name
- Common Name: Capybara
- Scientific Name: Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris
o
o
Distribution and Habitat
- Capybaras are distributed throughout the basins of the Orinoco, Amazon, San Francisco and La Plata Rivers. Water and temperature are the main factors in its distribution.
- Its range covers the countries of Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Ecuador, Colombia, French Guiana, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay and Venezuela.
- Capybaras live in lowland habitats near water sources. Its habitat includes forests, wetlands, mangrove swamps and riverbanks.
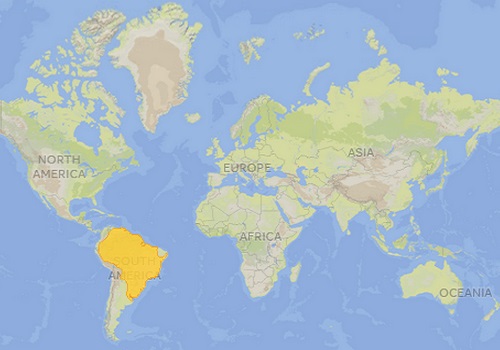
Capybara Distribution Map. Source: IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
Physical Features
- The capybara is the largest living rodent.
- Females are slightly larger than males.
- It has a large and heavy body covered with coarse red-brown, light brown to light yellow-grey hair. Hair length ranges from 1.18 to 4.72 in or 30 to 120 mm.
- Limbs are short and digits have partial webbing. Forefeet has four digits and hindfeet three.
- Capybaras have broad head and short and rounded ears.
- These rodents weigh from 77 to 145.5 lb or 35 to 66 kg and are about 4 ft or 1.2 m long.
Behavior
- Capybaras live in herds of an average of 7 individuals during rainy season and 16 during the dry season. The number in a herd is affected by the condition of habitat and not by season.
- During drought groups capybara herds, made up of hundreds of animals, congregate around water sources.
- Herds are formed by a dominant male, females with offspring and few subordinate males.
- Capybaras live in home ranges averaging 10 hectares but spend most of the time in a small area of less than 1 ha.
- They mark their home range with scents from their nasal and anal glands.
- During the morning they rest by the water under shade. During the hottest part of the day they roll about or lie relaxed in mud holes or water.
- They are slow and selective grazers and spend several hours in this activity.
- Capybaras are semi-aquatic and are good swimmers.
Diet
- Capybaras are herbivores.
- They are grazers and feed mainly on grasses and aquatic plants. They also eat seeds, grains, nuts, fruits, leaves, stems, and bark.
Reproduction
- Male and female capybaras reach reproductive maturity at 18 months.
- They bread throughout the year but it peaks at the beginning of the rainy season. They are polygynous.
- Gestation lasts up to 120 days.
- Litter size is 1 to 7 with an average of 3.5.
- The young are weaned at 3 months and stay with their mother until they are about 1 year old.
Life Expectancy
- Average lifespan in the wild is 6 years but they can live up to 10.
- In captivity they can live up to 12 years.
Predators
- Capybaras, especially the young, are at risk of predation by green anacondas (Eunectes murinus), vultures, feral dogs, jaguars (Panthera onca) and caimans (Caiman crocodilus).
- Humans hunt adult capybaras for its meat and hides.
Threats
- Its main threat is the loss of habitat due to water contamination from to mining and oil exploration activities.
Conservation Status
- The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species lists the capybara as a least concern species due to its wide distribution and large population unlikely to decline.
- They occur in many protected areas however some local populations are in decline due to over-hunting.
Did you know?
Capybaras are closely related to guinea pigs and rock cavies.
References and further research
The American Society of Mammalogist – Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris
The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
University of Michigan Museum of Zoology – Hydrochoerus Hydrochaeris
Eartham College Biology Department – Capybara
Denver Zoo – Capybara Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris



