0
Taxonomy

Cheetahs from the National Zoological Gardens of South Africa. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species considers this species as vulnerable.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Carnivora
- Family: Felidae
- Genus: Acinonyx
- Species: Acinonyx Jubatus
0
Name
- Common name: Cheetah, hunting leopard.
- Scientific name: Acinonyx Jubatus.
Physical Features
- Cheetahs have coarse short tan fur with black one inch black spots that serve as camouflage.
- They are distinguished from other big cats by their smaller size, spotted fur, small heads and ears and their “tear stripes” that go from the corner of the eyes to the side of the nose.
- When running at high speed cheetahs use their tails to steer.
- Cheetahs are the fastest land mammals on earth. They can run as fast as 70 to 75 mph or 112 to 120 km/h. They have the ability to accelerate from 0 to 60mph or 0 to 100 k/h in 3 seconds which is 4 times faster than humans.
- Cheetahs have enlarged hearts and lungs which uses oxygen more effectively during their fast chases.
- Their paws are semi-retractable which offers additional grip. Semi-retractable paws are known only in other three cat species: the fishing cat, the flat headed cat and the Iriomote cat.
- Some cheetahs with large blotchy merged spots are called “King Cheetahs”. They are a rare mutation.
Size and Weight
- Adult cheetahs weight from 46 to 159 lbs or 21 to 72 kg. Their body length ranges from 43 to 59 in or 60 to 84 cm. Their height ranges from 26 to 37 in or 66 to 94 cm tall at shoulder level.
Distribution and Habitat
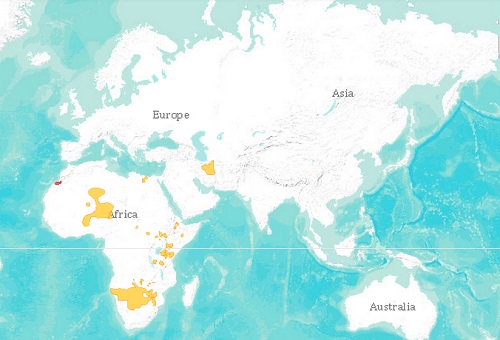
- Cheetas (Acionyx jubatus) inhabit most of Africa and parts of Iran. They live in open and vegetated savannas.
Predators
- Cheetahs use their speed as the only way to escape its predators. Among them are lions, leopards, hyenas and African wild dogs.
Breeding
- They are difficult to breed in captivity.
- Cheetahs mate throughout the year. Gestation period is about 90 days. The average litter is from 2 to 4 but they can have up to 9 cubs.
- Cubs have a mortality rate of 50 to 75% because they are prey to larger animals.
- Pups are born with spots unlike other cats, and with fur on their necks called “mantie” which they shed when they get older.
- Pups leave their mothers after one and a half to two years after their birth. During this time they learn how to hunt and survive.
Social Behavior
- Males live in groups and may stay together for life, while females are solitary unless they are raising pups.
- Males mark their territory by urinating on objects such as trees. Females do not mark their territory but have a home range.
- Cheetahs can purr but cannot roar.
Life Expectancy
- Cheetahs live an average of 12 years in the wild and up to 20 years in captivity.
Diet
- Cheetahs are carnivore and use their exceptional vision to scan for preys. They usually hunt early morning or late evening when it is still clear. They eat gazelles, wildebeest calves, impalas and other small and medium size animals.
- They drink once every 3 to 4 days.
- During a hunt the cheetah trips its pray and then bite it on the throat to suffocate it. They rely on tall grasses for camouflage while hunting. About 50% of chases are successful and they last from 20 to 60 seconds. They will drag their prey to protect it from other animals.
Threats
- Habitat destruction due to human encroachment.
- High cub mortality rate, cubs are prey to lions and hyenas.
- Their gene pool has very low variability due to inbreeding, this means that the ability of its population to adapt to environmental changes is reduced.
Conservation Status
- The IUCN – International Union for Conservation of Nature- lists cheetahs as a “vulnerable” species.
Did you know?
- Cheetahs have been extinct in India since 1940.
.