Interesting Facts
- Tokyo Tsukiji Market is the largest wholesale market of Southern blue fish tuna. In 2013 a 222 kl tuna was sold for $1.8 million or $8,000 a kilogram.
- This species was previously considered as a subspecies of the Atlantic Bluefin Tuna (Thunnus thynnus) or the Pacific Bluefin Tuna (Thunnys orientalis).
- Recreational and game fishers of Southern Bluefin Tuna is allowed in Australia and its catch is regulated by legislation.
- Bluefin tuna migrate vertically and horizontally.
Taxonomy

Southern Bluefin Tuna. Photo: Greenpeace / Roger Grace
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Actinopterygii
- Order: Perciformes
- Family: Scombridae
- Genus: Thunnus
- Species:
- Thunnus maccoyii
Name
- Common Name: Southern Bluefin Tuna
- Scientific Name: Thunnus maccoyii
0
o
Population and Conservation Status

- The Southern Bluefin Tuna is considered Critically Endangered by the IUCN.
- According to the Commission for the Conservation of Southern Blue Tuna (CCSBT) there has been a 85.4% decline in spawning stock over the past 36 years and there is no sign that it is rebuilding.
- The CCSBT formalizes allowable quota limits for its members and cooperating countries.
- Australia is the only country with Southern blue fin tuna fisheries where Immature fish of 2 to 4 years are removed from the wild and taken to farms. In Australia the species is listed as Conservation Dependent under the EPBC Act.
- According to the Department of the Environment and Energy of the Australian Government there were an estimated 460,000 mature individuals of Southern Bluefin Tuna in 2009. The species is considered to have a single global population.
Distribution and Habitat
- This species is found in the temperate and cold seas of the southern hemisphere. They are distributed throughout the south Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans at depths of 164 to 9,000 feet (50 to 2,743 meters). Their range extends from about 30 to 50ºS.
- Southern Bluefin Tuna is a highly migratory species associated with age and feeding patterns.
- Spawning happens at a small area in the Indian Ocean near Java and northwest of Australia. The spawning season is from September to March at water temperatures 68 to 86ºF (20 to 30ºC).
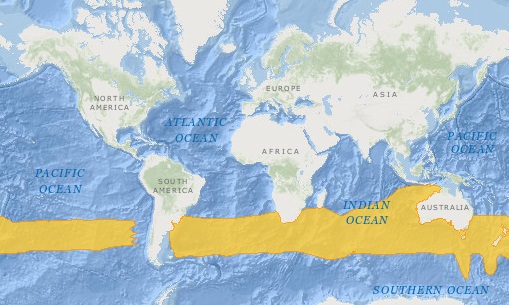
Southern Bluefin Tuna Distribution. Map adapted from IUCN.
Physical Features
- Bluefin tunas are built like torpedoes, they have streamlined bodies built for speed. They can retract their dorsal and pectoral fins to reduce drag.
- Its skin in metallic blue on top and silver on the bottom. Its coloring serves as camouflage.
- They have the ability to keep their bodies warm, unlike most fish.
- They are the smallest of the bluefin tunas. The southern species can grow up to 7.39 feet (2.25 meters) long and weigh up to 441 lbs (200 kg).
- The physical difference between the Southern Bluefin (Thunnus maccoyii) and the Atlantic Bluefin (Thunnus Thynnus) is that the latter has darker median caudal keel. It is yellow in the southern species. The pectoral fins in adult Southern Bluefin tunas are larger in the Atlantic species.
Behavior
- Bluefin tuna is a voracious feeder with high metabolic needs. It feeds on anchovies, sauries, hakes, squid, shrimp and crabs.
- The migrate between tropical and cool waters in search for food. Their migration depends on age and feeding needs.
- They can reach speeds of up to 43 miles (70 km) per hour.
- When it is not spawning season they congregate in the open sea to form feeding aggregations.
- The adult Bluefin is a pelagic fish, they live in the open sea neither close to the bottom nor near the shore. They group together in schools based on size and not on species. It is common to see blue fin tunas with many different species in a school.
Reproduction
- This species of tuna mature between 9 to 12 years old.
- Spawning happens at a small area in the Indian Ocean near Java and the northwest of Australia. The spawning season is from September to March at water temperatures 68 to 86ºF (20 to 30ºC).
- Females lay from 14 to 15 million eggs in a spawning season, between September and April. Eggs hatch between 2 to 3 days.
Life Expectancy
- Southern blue fin tuna has a live expectancy of at least 20 years.
Predators
- Predators includes sharks, orca or killer whales and humans.
References and further research
- International Commission for the Conservation of Atlantic Tunas
- Commission for the Conservation of Southern Bluefin Tuna
- Australian Government Department of Environment and Energy – EPBC Act
- Department of the Environment and Energy of the Australian Government
- Inter-American Tropical Tuna Commission
- IUCN Red List of Threatened Species – Southern Bluefin tuna thunnus maccoyii
- World Register of Marine Species
- The Animal Aging and Longevity Database
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Organization
- Tuna Research and Conservation Center
- International Game Fish Association
- Greenpeace International
- Australian Fisheries Management Authority – Southern Bluefin Tuna Fishery
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations – Fisheries and Aquaculture Department